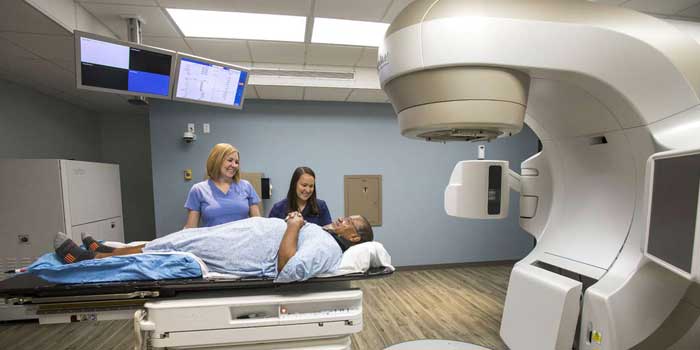
- Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is an advanced form of radiation therapy that delivers a high dose of radiation to a precise target within the body.
- It is used to treat various types of cancer, particularly those located in the lung, liver, spine, and other areas where precision and accuracy are critical.
- One of the key advantages of SBRT is its ability to deliver a concentrated dose of radiation to the tumor while minimizing the exposure of surrounding healthy tissues.
- This is achieved through advanced imaging techniques and computerized dose calculations, allowing for highly precise targeting of the cancerous cells.
- In SBRT, a patient's body is immobilized to ensure minimal movement during treatment.
- High-resolution imaging, such as CT scans or MRI, is then used to precisely locate the tumor and surrounding organs.
- This detailed imaging data is then used to create a treatment plan that delivers multiple, highly focused radiation beams from different angles, converging precisely on the tumor.
- This allows for a high dose of radiation to be delivered to the tumor while minimizing the impact on healthy tissues.
- The delivery of the high radiation dose in just a few treatment sessions is another key advantage of SBRT.
- Traditionally, radiation therapy involves numerous treatments over several weeks which lead to inconvenience to patients.
- SBRT can often be completed in as few as one to five sessions, offering convenience and reduced overall treatment time for patients.
- Additionally, SBRT may be used as a primary treatment or in combination with other therapies, such as surgery or chemotherapy, depending on the specific characteristics of the cancer and the individual patient.
- The effectiveness of SBRT in cancer treatment has been demonstrated in numerous clinical studies and trials.
- It has shown promising results in terms of tumor control and overall survival rates, particularly for early-stage lung cancer and certain types of prostate cancer, liver and spinal tumors.
- As with any cancer treatment, there may be potential side effects associated with SBRT, including fatigue, skin reactions, and changes in the treated area.
- However, the risk of damage to healthy tissues is minimized due to the precision of the treatment, and these side effects are often temporary and manageable.
- In summary, SBRT is a highly advanced and effective form of radiation therapy that offers precise and concentrated treatment to cancerous tumors while minimizing impact on surrounding healthy tissues.
- Its ability to deliver high doses of radiation in a few treatment sessions and its potential for excellent tumor control make it a valuable option for many cancer patients.
Overall, radiotherapy plays a critical role in the management of brain tumors, offering the potential to control tumor growth, relieve symptoms, and improve patient outcomes. The decision to pursue radiotherapy and the specific approach used will be guided by a patient’s medical team based on the unique characteristics of the tumor and the patient’s overall health. With ongoing advancements in treatment techniques and supportive care, the aim is to maximize the effectiveness of radiotherapy while minimizing potential side effects, ultimately contributing to improved outcomes and quality of life for patients with brain tumors.
For further information regarding cancer treatment
Reach our specialist at I CARE CANCER CLINIC
or Contact +91 8939 8939 95.