Uterus Cancer
You are here:
- Home
- Uterus Cancer
Overview
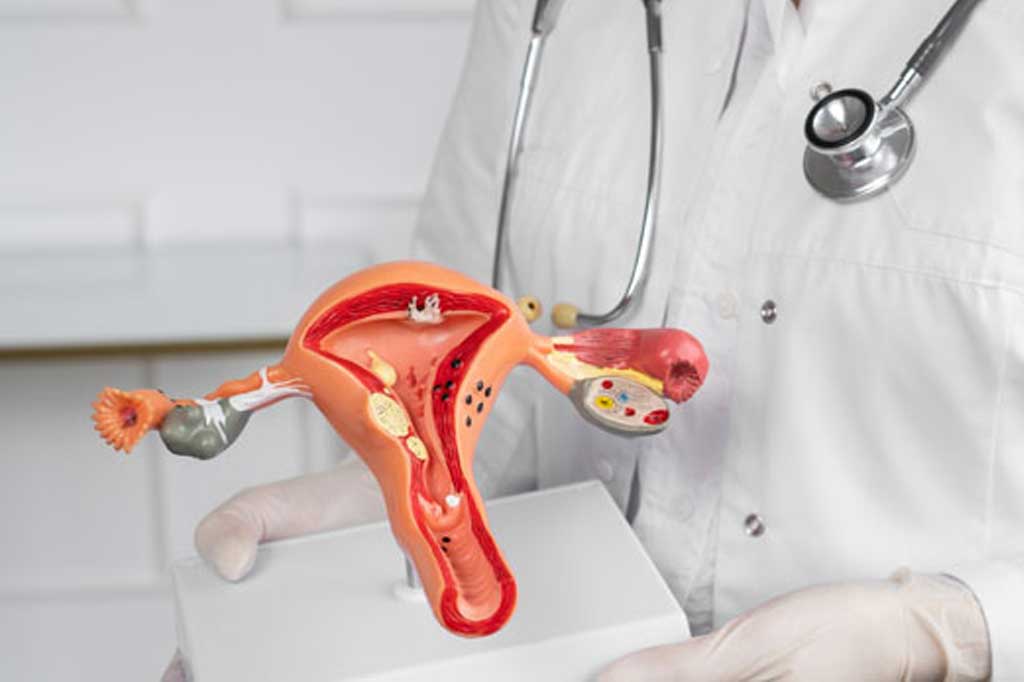
Uterus is a female reproductive organ, located in the lower portion of abdomen. It plays a major role in mensturation, fertility, and pregnancy. The ovaries that produce eggs are attached to the upper portion of the uterus through fallopian tubes. The inner most lining of the uterus is called the endometrium and the muscular lining of uterus is the myometrium, and the thin outer most layer of the uterus is the serosal layer. The lower portion of the uterus is in continuation with cervix which opens Into vagina. The cancers that arises from the lining of the uterus are addressed as Endometrial cancers. Cancer that develop from muscles (myometrium) are called as uterine sarcoma that are rare in its presentation.
Endometrial carcinoma
Types of uterine malignancy
Endometriod adenocarcinoma is the most common histopathological subtype, it accounts for more than 83 % of uterine cancers. There are also some rarer type of endometrial cancer that includes Papillary serous ( 4-6% ), Clear cell carcinoma ( 1-2% ), Mixed mullerian tumours.
Risk factors associated with endometrial carcinoma :
There are multiple risk factors known to increase the chances of malignancy in individuals that includes:
- Obesity may increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
- Type 2 diabetes is considered as one of the cause
- Having Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Consumption of high fatty diet
- A Family history of endometrial cancer in first degree relatives( Mother/siblings)
- Having certain genetic condition like hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer(HNPCC)
- Taking a Hormonal tablet Tamoxifen for breast cancer treatment, as such increases the risk of endometrial cancers.
-
Exposureto endometrial tissue with prolonged estrogen which can be due to
- Early menarche
- Delayed menopause
- Nullparous women
Elderly age as itself is considered as the main risk factors for most of the cancers, and as theage advances the chances of getting cancer increases.
Endometrial Biopsy:
Once the ultrasound confirms any abnormality in endometrial lining a sample from the endometrial lining needs to be sent for histopathology to look for any abnormality. Endometrial Biopsy can be performed in different ways
Endometrial pippelle
It’s an office procedure, which is very quick and well tolerated by the patients, and they are quite very sensitive for making the diagnosis, it is done by introducing a thin flexible tube through cervix into the uterus , endometrial lining is sampled and sent for If thereis no endometrial pathology in the specimen sent and if patient become asymptomatic no further test is required
Hysteroscopy
It is done under sedation using a scope which is negotiated into the endometrial cavity and Biopsy from the abnormal area is done under vision.
Dilatation and curretage (D&C)
The role of D & C is probably very limited as the diagnosis can be made easily with the office procedure using endometrial pipelle. Dilatation and curretage is usually done under anaesthesia, it is necessary in patients who are bleeding and have a stenotic ( closed ) cervical opening
MRI abdomen and pelvis
Once a diagnosis of uterine malignancy is made an local imaging of pelvis and abdomen is done. MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging ) of the pelvis gives a picture about the uterine lesion , it’s depth of invasion,and local infiltration along with details about any nodal involvement
Tests used to diagnose endometrial cancer:
- Physical examination and history : A history of duration of symptoms, patients health habits and past illness and treatment are taken by the specialist along with general clinical examination
- Ultrasonography (Transabdominal/ Transvaginal) : used to look for endometrial thickness / any mass in endometrial cavity
Common clinical presentation for endometrial cancers
- Most common presentation being a post menopausal bleeding
- Other common presenting complaints includes heavy and frequent menstural bleeding with intermenstural bleeding.
- Difficult or painful urination
- Pain in pelvic (lower abdomen) area
- Abnormal discharge per vagina
Stages of Endometrial carcinoma
The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) is one of the common staging system used for all gynaec malignancy

- Stage I: It is restricted to tumours confined to the uterus, with non aggresive histological types
- Stage II : Tumour extends to lower uterine segment (cervix) with deep stromal infiltration
- Stage III : Tumour involves local spread / nodal involvement
- Stage IV : Tumour infiltrates adjacent structures ( bowel and bladder ) / distant metastasis ( lung/ liver
Treatment option for endometrial cancer
Surgery
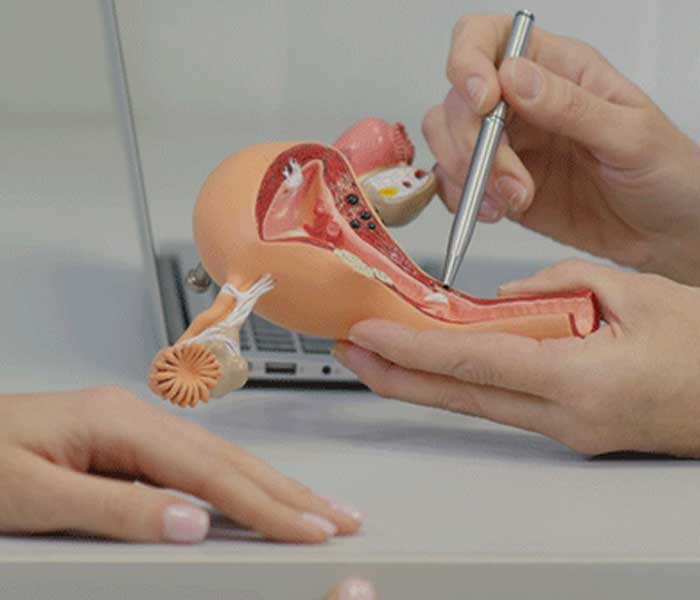
Surgery is the most common treatment for endometrial cancer. That includes removal of uterus including cervix and ovaries along with regional lymphnodal dissection , this could be done either minimal invasive surgery( laproscopy/ robotic) or by open approach.

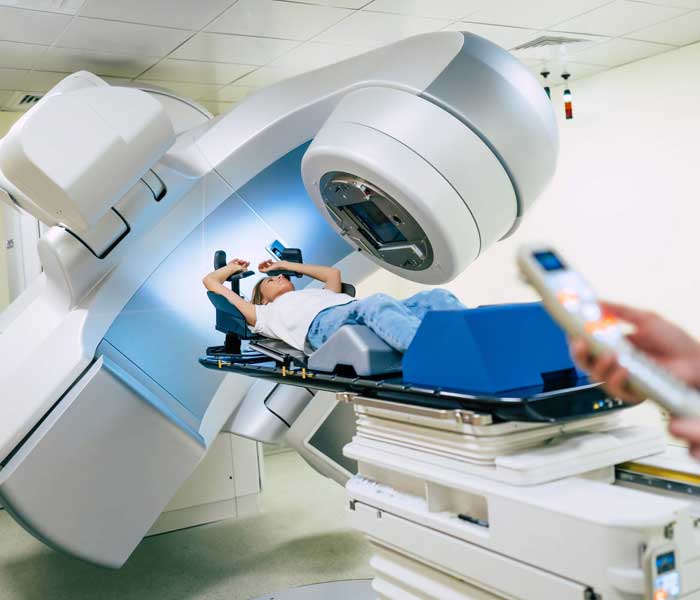
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high energy X rays to kill any residual cancer cells. There are two types of radiation therapy, the way radiation therapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer after complete Surgical staging is done.
- External beam radiation is uses a machine outside the body to send radiation to the area of the body that is affected by cancer(pelvis)
- Brachytherapy where the catheter are placed inside the vagina and the radiation is delivered in close contact with the affected part.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a systemic therapy, that are used to stop the growth of cancer cells. It is delivered through the veins , the drugs enters the blood stream and reaches the cancer cells through out the body.
The administration of Chemotherapy in endometrial cancer depends on the type and stage of the endometrial cancer being treated.
For further information regarding cancer treatment
Reach our specialist at I CARE CANCER CLINIC
or Contact +91 8939 8939 95.
