Cervical Cancer
- Home
- cervical cancer
Overview
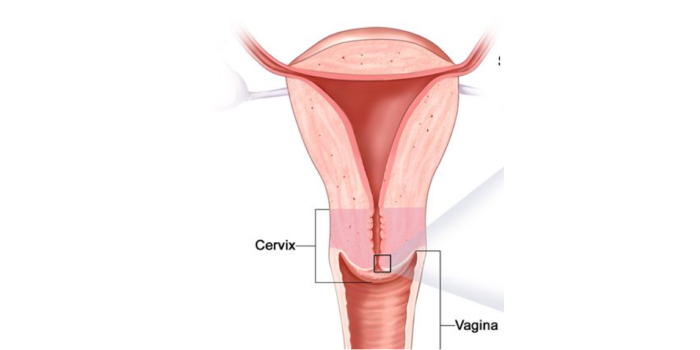
Cervix is the lower part of the uterus that connects the uterus (womb) to the vagina (birth canal). An abnormal growth of cells in the lower portion of the uterus (Cervix) leads to cervical Cancer. Before cancer appears in the cervix the cells go through various changes known as dysplasia, these changes if not treated on time, the abnormal cells may become cancer cells which may start to grow and spread to adjacent structures and to distant site.
Types of Cervical Cancer
There are different type of cancer cells that can form in cervix, the most common cancer are Squamous cell Carcinoma of cervix, Other types includes adenocarcinoma, adenosquamous and clear cell carcinoma.
Symptoms
- Bleeding per vagina between periods, post coital or after menopause
- Watery discharge per vagina and a have a foul odor
- Pelvic pain or lower abdominal pain
- Urinary symptoms like dysuria or blood in urine
- Difficult or painful bowel movements
Causes
Human Papilloma virus (HPV) infection : Is considered as one of the major risk factor for cervical
- Persistent infection with HPV causes cervical cancer.
- The two most common high risk types HPV 16 and HPV 18 causes 70% of cervical cancer.
- Nearly all women who are sexually active get infected with HPV at some point of their life, most of the infections are self-limiting.
- When a high risk HPV infection last for many years and if left untreated, it may result into cervical cancer
-
Other associated factors that increase the risk of cervical cancer involves:
- Smoking
- Weakened immune system
- Poor personal Hygeine
HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE CERVICAL CANCER?
It’s an office procedure in which a small brush is used to gently remove cells from the surface of cervix
Colposcopy
This is done when your doctor suspects any abnormality in the cervix on visual inspection or if there is any abnormal Pap smear report
Biopsy
It’s a procedure where a small tissue is removed from the cervix to be examined by the pathologist under microscope.
Imaging
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Used an assessment tool to look for local extent of the disease involvement
- PET CT: It’s a whole body scan done to look for local involvement of the primary disease and distant metastasis
Prognosis of cervical cancer
Prognosis depends on various factor like
- Stage of cancer
- Histological type of cancer (Squamous or adenocarcinoma)
- Age and general health of the patient
When Cancer detected at an early stage, the 5year survival rate is up to 91%
TREATMENT
The Cancer team involving surgical oncologist, medical and a radiation oncologist will work together and decide the plan of management for an individual patient based on the age, stage, and type of cancer and also based on general health condition of the patient.
SURGERY
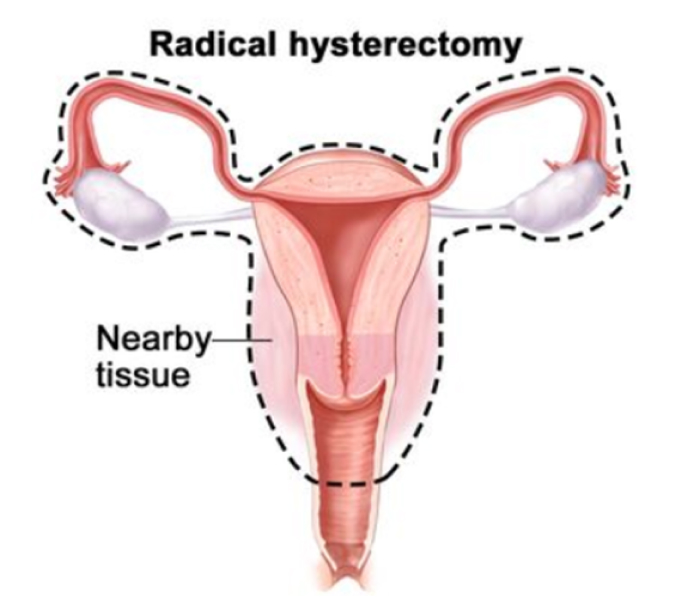
- Radical Hysterectomy is usually done for very early stage small cancer confined to cervix.
- It involves removal of uterus, cervix and upper part of vagina along with tissues and ligaments around the uterus and cervix
- With removal of both ovaries and tubes along with pelvic nodes
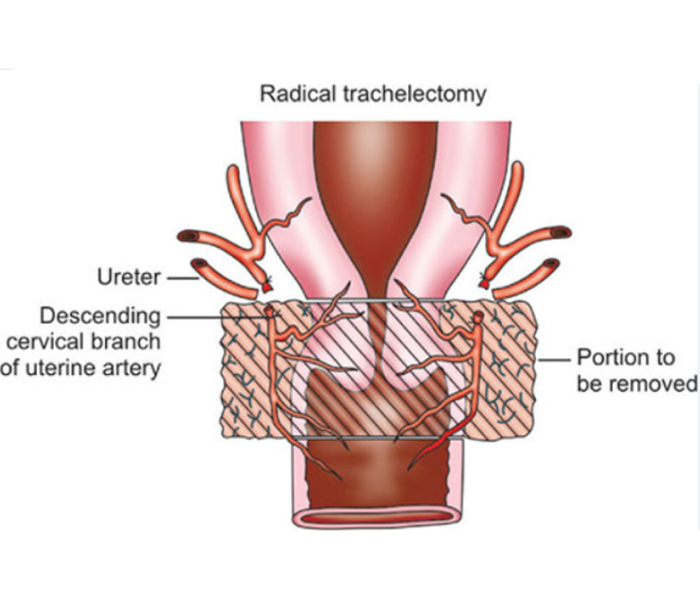
- It’s a procedure usually done in young women desiring fertility
- It involves removal of cervix with adjacent structure along with removal of pelvic nodes.
RADIATION THERAPY
It uses high energy X Rays or radiation to kill cancer cells. They are most commonly used in management of advanced cervical cancer or in an early stage elderly patient who are not fit for any surgical procedures.
The main two type of radiation involves
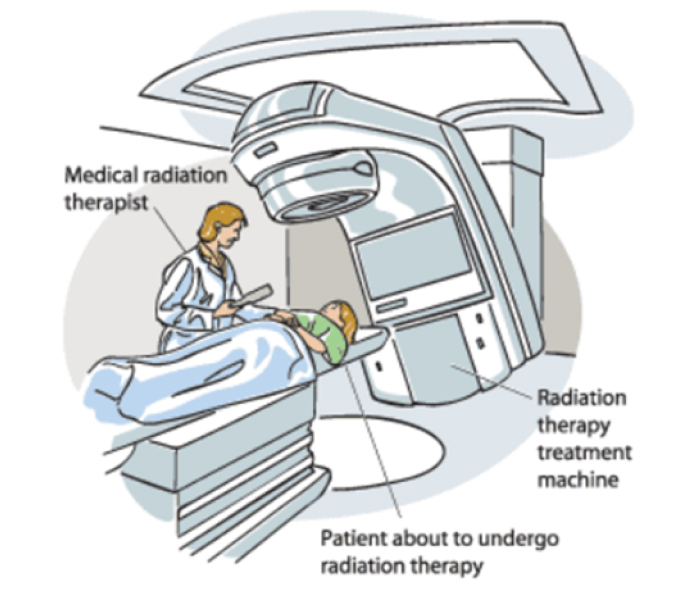
External beam radiation
There are various types of external beam radiation, which irradiates the tumour sparing the normal tissues and commonly used radiations are
- 3-D conformal radiation therapy
- Intensity modulated radiation therapy(IMRT)
- Image guided radiation therapy(IGRT)
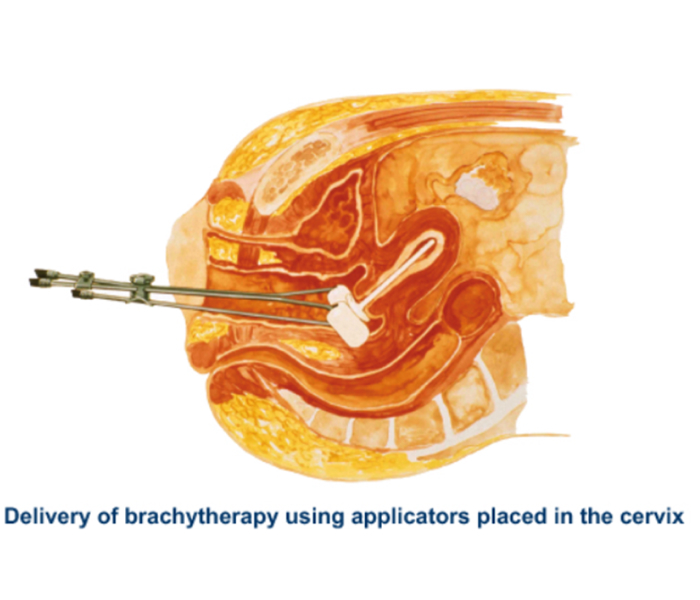
Internal radiation therapy:
(also known as brachytherapy)
Uses a radioactive substance sealed in needles/wires/catheters that are placed directly into vagina near the cancer cells in cervix.
CHEMOTHERAPY
It’s a systemic therapy, where drugs are used to kill the cancer cells, they are given in combination with radiation or alone based on the stage and type of cancer.
IMMUNOTHERAPY
It helps by boosting a person’s immune system to fight against cancer. Patients whose tumor cells produce PD-L1 biomarker can be treated with Pembrolizumab.
