Chemo port
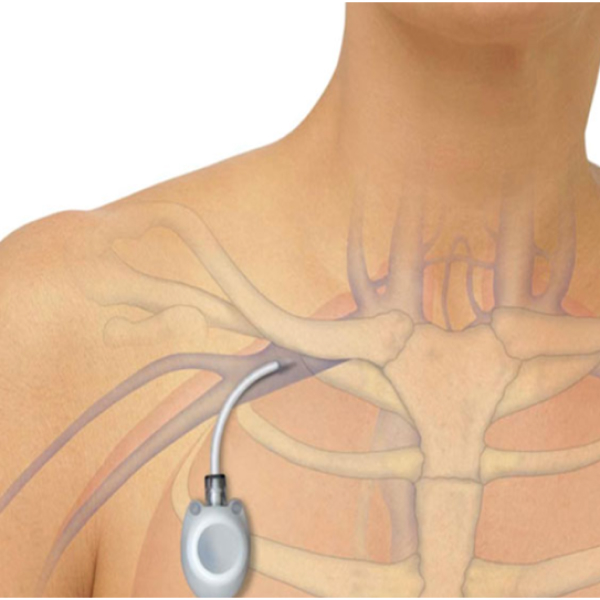
Chemo Port Placement
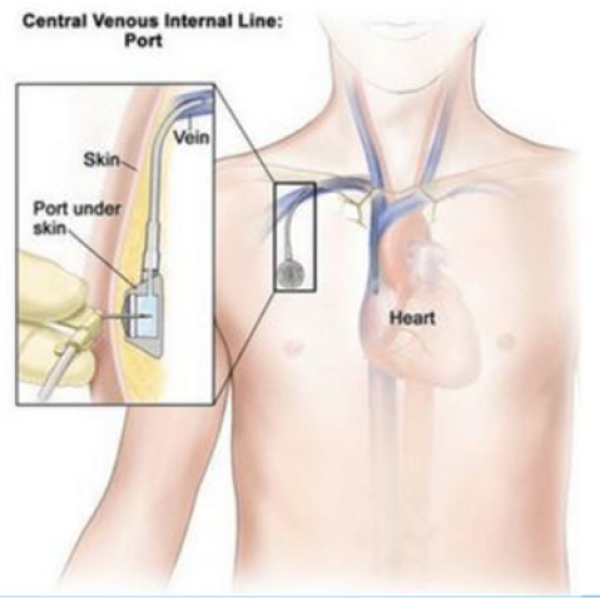
Chemo Port Insertion Procedure
- Preparation: The patient is sedated to ensure comfort during the procedure.
- Accessing the Vein: A small cut is made in the neck or upper chest to access the vein.
- Inserting the Tube: A small opening is created in the vein, and the silicone tube is inserted.
- Creating the Pouch: A subcutaneous pouch is created in the upper chest wall where the chemo port is placed.
- Closing the Opening: The opening is closed with stitches.
- Post-Procedure Check: An X-ray is taken to ensure the chemo port is correctly positioned.
The entire procedure typically takes about an hour, and patients can usually be discharged home on the same day.
Benefits of a Chemo Port
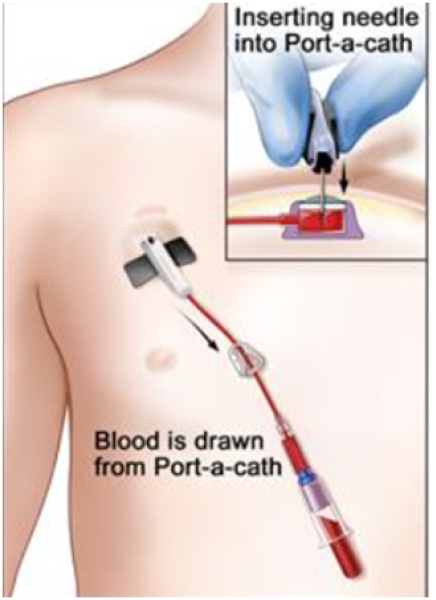
- Delivery of Fluids and Transfusions: The port can be used to administer fluids and blood transfusions, making it a versatile tool in patient care.
- Blood Draws: It simplifies the process of drawing blood for lab testing, reducing the need for repeated needle sticks.
- Imaging Procedures: The port can be used to inject dye for PET and CT scans, facilitating diagnostic procedures.
- Long-Term Use: The port can remain in place as long as necessary, providing continuous access for treatments.
Potential Risks of Chemotherapy Ports
While chemo ports are generally safe, there are some risks associated with their use:
- Thrombosis: Blood clots can form and block the catheter, necessitating medical intervention.
- Mechanical Issues: The catheter may move out of place, which can compromise its functionality.
- Infection: Although rare, infections can occur and require immediate removal and replacement of the port.
- Chemo Port Removal: Unlike the insertion, the removal of a chemo port does not need sedation. Local anesthesia is administered over the scar site, an incision is made, and the port is released from surrounding tissue and removed. Patients may experience mild discomfort or swelling, which typically resolves in a few days.
Chemo Port Maintenance and Care
- Keep the Area Clean: Regularly clean the skin around the port to prevent infections.
- Monitor for Signs of Infection: Watch for redness, swelling, or discharge around the port site and report any concerns to your healthcare provider.
- Follow Medical Advice: Adhere to the guidelines provided by your healthcare team regarding port care and maintenance.
Conclusion
Chemo ports play a vital role in the effective administration of chemotherapy. They provide a safer, more efficient way to deliver medications, fluids, and other treatments while reducing the discomfort associated with repeated needle sticks. Understanding the procedure, benefits, and risks associated with chemo ports can help patients and their families make informed decisions about their cancer treatment.
By considering the detailed information provided in this guide, patients can better prepare for the use of a chemo port and manage their care effectively. This comprehensive approach ensures that the benefits of the device are maximized while minimizing potential risks.